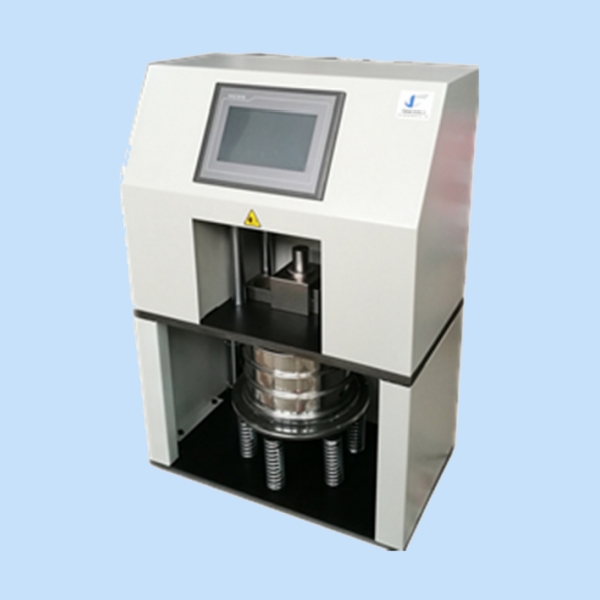
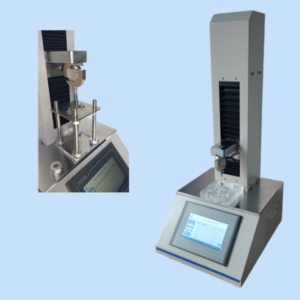
GHR-01A Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester
- Standard: ISO 719, ISO 720
- Manufacturer: Cell Instruments
- Applications: Packaging materials, medical device materials, pharmaceutical testing, and more.
- Customization: Available for special testing requirements and automation transformations
The Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester is an essential instrument in the testing and evaluation of glass materials used in pharmaceutical and medical packaging. This test helps determine how well glass resists degradation when exposed to water, ensuring that pharmaceutical products remain safe and effective throughout their shelf life. The hydrolytic resistance of glass is crucial, particularly in packaging such as ampoules, vials, and infusion bottles, where even minimal interaction between the glass and its contents can compromise the stability and safety of medications.
The GHR-01A Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester is designed to provide accurate and efficient testing according to international standards such as ISO 719 and ISO 720, making it an indispensable tool for quality control and regulatory compliance in the pharmaceutical industry.
I. Importance of Hydrolytic Resistance in Medical Glass Packaging
Hydrolytic resistance refers to the ability of glass to withstand degradation or chemical interaction when exposed to water. This is particularly critical in pharmaceutical packaging, where leaching of elements from the glass can affect the purity, efficacy, and safety of the product. For medical-grade glass used in the production of ampoules, infusion bottles, and other containers, ensuring a high degree of hydrolytic resistance is a primary concern. The Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester plays a pivotal role in determining this resistance by simulating exposure to water at elevated temperatures and measuring the glass’s reaction.
II. Test Methods for Hydrolytic Resistance
The Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester follows the procedures outlined in ISO 719 and ISO 720, which describe the test methods for evaluating hydrolytic resistance at different temperatures.
- ISO 719: Specifies the test method for hydrolytic resistance of glass grains at 98°C. This standard classifies glass materials based on their chemical durability when exposed to water at this temperature.
- ISO 720: Outlines the test method for hydrolytic resistance at 121°C, providing a higher level of stress on the glass grains to assess their resistance under more extreme conditions.
III. Step-by-Step Process:
Sample Preparation: Glass grains are prepared by crushing glass into fine particles using the GHR-01A Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester. The automatic crushing system ensures consistency in particle size, which is critical for accurate test results.
Sieving: After crushing, the glass grains are automatically sieved to separate qualified samples from waste material. The GHR-01A’s vibratory sieving mechanism ensures precision in selecting the proper particle sizes for testing.
Testing: The selected glass grains are exposed to water at the required temperature (98°C or 121°C) as per the ISO standards. The tester simulates prolonged exposure to water, and the hydrolytic resistance of the glass is measured by assessing the extent of degradation.
Result Analysis: After the test, the degree of glass grain degradation is measured by evaluating the release of soluble elements. The results are classified according to the standards set by ISO 719 and ISO 720, helping manufacturers determine the suitability of the glass material for pharmaceutical applications.
IV. Features and Benefits of the GHR-01A Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester
The GHR-01A Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester is designed with advanced features that ensure accuracy, safety, and efficiency during the testing process:
Automation for Precision: The tester combines automatic glass crushing and vibratory sieving, reducing manual handling and ensuring consistent particle size selection for testing.
User-Friendly Interface: The instrument features an intuitive HMI screen for easy operation, allowing technicians to manage the testing process with minimal effort.
Enhanced Safety Measures: The GHR-01A is equipped with safety devices to protect users from glass splatter during crushing and sieving. It also has automatic shutdown features to prevent accidents during operation.
Eco-Friendly Design: The tester includes a built-in waste collection system that safely disposes of glass fragments, minimizing environmental impact.
Compact and Efficient: Its vertical design reduces space requirements and enhances gravitational separation of larger samples, improving test efficiency and accuracy.
V. Technical Specifications of the GHR-01A Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester
| Mortar/Pestle Dimension | Φ50/Φ48 mm |
| Sieve A Aperture | 425μm |
| Sieve B Aperture | 300μm |
| Sieve O Aperture | 600μmμm |
| Sieve Shaking Duration | 5min |
| Gas Pressure | 0.5 Mpa |
| Gas Port Size | Ф6 mm |
| Power | AC 110~220V 50Hz |
VI. Understanding ISO 719 and ISO 720 Standards
The ISO 719 and ISO 720 standards are internationally recognized guidelines for testing the hydrolytic resistance of glass. These standards ensure that the glass used in pharmaceutical packaging meets the necessary quality and safety requirements.
ISO 719: Specifies the test method at 98°C. Glass grains are exposed to water at this temperature, and the amount of leachable material is measured to classify the glass.
ISO 720: Increases the test temperature to 121°C, subjecting the glass grains to more extreme conditions. This standard is used to assess glass materials that need to endure higher stress environments.
Both standards are crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of pharmaceutical packaging materials.
FAQs
1. What is the Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester used for?
The Glass Grain Hydrolytic Resistance Tester is used to evaluate the hydrolytic resistance of glass materials, particularly in medical and pharmaceutical packaging. It determines how well glass resists degradation when exposed to water.
2. Why is hydrolytic resistance important for pharmaceutical packaging?
Hydrolytic resistance ensures that the glass does not release harmful elements into pharmaceuticals, maintaining the integrity and safety of the medications.
3. How do ISO 719 and ISO 720 relate to hydrolytic resistance testing?
ISO 719 tests the resistance of glass grains at 98°C, while ISO 720 tests at a higher temperature of 121°C. Both standards provide classifications for glass materials based on their durability against water.
4. What safety features does the GHR-01A offer?
The GHR-01A is equipped with safety devices to protect users from glass splatter, as well as automatic shutdown features to ensure operational safety.
5. How does the GHR-01A improve testing efficiency?
The GHR-01A integrates automatic crushing and sieving, reducing manual labor and ensuring consistent and precise sample preparation for accurate testing results.